Clearance on a 3D printer refers to the amount of space between the nozzle or extruder and the printing bed or platform. It is important to have the correct clearance to ensure proper adhesion and layer height for the print. If the clearance is too high, the print may not adhere properly to the bed and if it is too low, the nozzle may scrape against the bed or damage the print. The clearance can be adjusted manually or automatically through the printer settings, and it is typically measured in millimeters or microns.
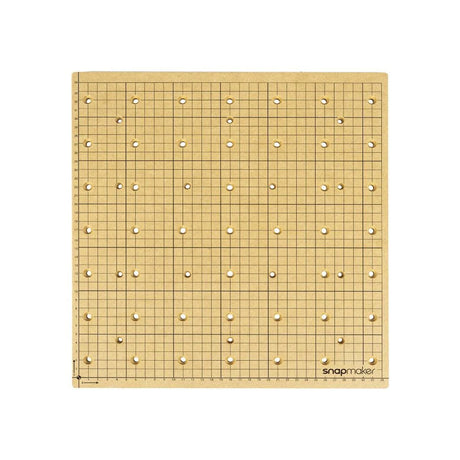
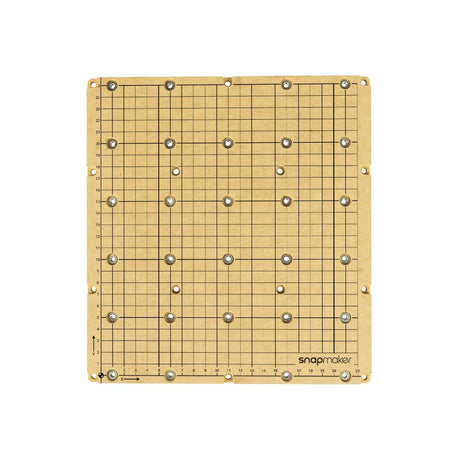
CNC Platform (MDF Wasteboard) for Snapmaker 2.0
From €11,50 EUR€22,99Unit price /UnavailableIn stock
What is clearance on a 3D printer?
What are some tips or best practices for beginners who are new to 3D printing and CNC, and how can they ensure success with their projects?
Here are some tips and best practices for beginners who are new to 3D printing and CNC:
1. Start with the basics: Before tackling complex projects, start with simple designs and get comfortable with the equipment and software.
2. Use high-quality materials: Use high-quality filaments and other materials for better print quality and durability.
3. Keep the workspace clean: Clean the workspace and keep the printer and CNC machine free from debris to prevent damage to the equipment.
4. Calibrate the equipment: Regularly calibrate the printer and CNC machine to ensure accurate and precise output.
5. Experiment with settings: Experiment with different settings such as temperature, print speed, and layer height to optimize print quality and efficiency.
6. Use support structures: When printing complex or overhanging shapes, use support structures to prevent the print from collapsing.
7. Practice good safety habits: Wear appropriate safety gear such as eye protection and gloves when working with 3D printers and CNC machines.
8. Join a community: Join online communities or local maker spaces to learn from other enthusiasts and get support with your projects.
By following these tips and best practices, beginners can ensure success with their 3D printing and CNC projects and develop their skills over time.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when starting out with 3D printing and CNC, and how can beginners troubleshoot issues that may arise during the process?
As a beginner, there are several common mistakes that you should avoid when starting out with 3D printing and CNC. Here are a few tips to help you avoid these mistakes:
1. Not calibrating your machine: Calibration is essential for getting accurate and consistent results from your 3D printer or CNC machine. Make sure to follow the calibration instructions carefully and adjust your machine as needed.
2. Incorrect bed leveling: If your bed is not level, it can cause adhesion problems and result in a failed print or cut. Use a level tool to ensure that your bed is flat and level before starting a print or cut.
3. Not using the right materials: Different materials have different properties and printing/cutting requirements. Make sure to use the right material for your project, and adjust your machine settings accordingly.
4. Ignoring support structures: Some 3D prints require support structures to help them maintain their shape and integrity. Make sure to include support structures where needed, and remove them carefully after printing.
5. Overheating the machine: Overheating can cause damage to your 3D printer or CNC machine. Make sure to monitor the temperature and avoid leaving your machine running unattended for long periods.
If you encounter issues during the process, you can troubleshoot them by checking the machine settings, making sure the machine is properly calibrated and leveled, ensuring that you're using the correct materials, and checking for any damage or wear and tear on the machine. Additionally, it can be helpful to consult online forums or communities for tips and advice from more experienced users.
Are there any online courses or tutorials that you would recommend for someone who is interested in learning about 3D printing and CNC?
Yes, there are many online courses and tutorials available for those interested in learning about 3D printing and CNC. Here are a few examples:
1. Udemy: Udemy offers a wide range of courses on 3D printing and CNC, ranging from beginner to advanced levels. The courses cover various topics such as 3D modeling, CAD software, slicing, and more.
2. Coursera: Coursera offers several courses related to 3D printing and CNC, including courses on CAD design and manufacturing, as well as a course on digital fabrication.
3. YouTube: YouTube has a vast library of videos and tutorials on 3D printing and CNC. There are many channels dedicated to these topics, such as Makers Muse, CNC Kitchen, and 3D Printing Nerd.
4. Instructables: Instructables is a website that offers step-by-step instructions for various DIY projects, including 3D printing and CNC. The website also has a community section where users can share their projects and ask for advice.
5. Snapmaker Academy: Snapmaker, the manufacturer of the popular 3-in-1 3D printer, CNC, and laser engraver, has an online academy that offers tutorials and courses on how to use their products effectively.
How much does it cost to start a 3D printing business?
The cost to start a 3D printing business can vary depending on various factors, such as the type of business model, the scale of production, the type of 3D printers and equipment, the cost of materials and supplies, and the cost of marketing and promoting the business. Generally, the cost to start a small 3D printing business can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the scale of production and the type of services offered. Some of the main costs to consider when starting a 3D printing business include:
1. 3D printers and equipment: Depending on the size and type of 3D printer required for the business, the cost can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Other equipment such as computers, software, and accessories may also need to be purchased.
2. Materials and supplies: The cost of materials and supplies, such as filaments, resins, or raw materials for CNC, can vary depending on the quality and quantity required for the business.
3. Business registration and legal fees: This includes costs such as registering the business, obtaining licenses and permits, and hiring legal services to protect the business.
4. Marketing and promotion: The cost of marketing and promotion can vary depending on the type and scale of the business, including costs such as website development, social media management, and advertising.
5. Operating costs: This includes the cost of rent, utilities, insurance, and other expenses associated with running a business.
It is important to conduct thorough research and create a detailed business plan to accurately estimate the costs of starting a 3D printing business.